Introduction
According to the Quarterly survey of Google’s SREs, engineers spend 33% of their time searching for information rather than designing, innovating, and building. Moreover, they are dealing with more complex designs, shorter timelines, and a growing number of digital tools.
In that regard, engineering data management can help you reduce the data chaos. Whether you are managing CAD files, revision histories, or BOMs across teams and tools, you need a way to keep things centralised, controlled, and accessible. Otherwise, you are just one step away from making a costly mistake.
So, what is engineering data management? Besides being a file storage, it is a system that organises, versions, secures, and shares every piece of engineering data across your organisation.
If you are an engineering manager, product designer, CTO, or part of a digital-first enterprise, you need to understand engineering data management.
So, let’s learn about it in this in-depth guide.
What is Engineering Data Management?

The process of collecting, storing, organising, and controlling all the data related to engineering design and development is called engineering data management. It covers CAD files, drawings, specifications, simulations, BOMs, and change orders.
It serves as the digital spine of your engineering team. This way, only the right people will have access to the right data at the right time, without any version mix-ups, delays, or errors.
When used effectively, it creates a single source of truth that drives collaboration, innovation, and speed.
History & Evolution of EDM
In the past, most data was stored in local folders or shared drives. Each team had its own way of organising files, and version control was often manual. As products became more complex and teams started collaborating globally, that approach did not scale.
The change happened with the release of the Product Data Management (PDM) systems. These helped engineers store and manage CAD files with basic version control. They were a step forward, but limited to design data.
As organisations needed more visibility and collaboration across departments, Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) emerged. Besides engineering, PLM system track and manage the entire product journey from concept to delivery.
That is where engineering data management found its role.
EDM evolved to solve a very specific challenge: managing the increasing volume, complexity, and interconnectivity of engineering data. Today, modern EDM systems integrate with CAD, PLM, and ERP platforms to give engineers complete control over their data, without slowing their innovation.
Importance of Engineering Data Management
In today’s engineering-driven industries, data is the new fuel. But without control, even the best data becomes a liability. That is why the importance of engineering data management cannot be overstated.
A reliable engineering data management system turns raw data into a strategic asset that drives efficiency, accuracy, collaboration, and innovation at every level.

Source: Acceldata
Let’s look at why EDM matters more today:
- Certifies data integrity and reduces errors- If you have ever dealt with the wrong version of a design file, you know that it is painful and expensive. Engineering data management keeps your data accurate, easy to track, and dependable across every stage of the project. With version control, audit trails, and centralised storage, your team can work with the most accurate and updated information. This reduces mistakes, removes confusion, and diminishes costly errors.
- Boosts cross-functional collaboration- When engineering, design, manufacturing, and quality teams work in silos, things low down. A strong engineering data management system breaks those barriers and provides a shared platform for teams to share and collaborate on real-time data. As a result, teams can collaborate more smoothly and make quicker and more informed decisions without unnecessary delays.
- Protects intellectual property and ensures compliance- Data leaks and non-compliance can damage a company’s finances and reputation. With engineering data management, sensitive design files and documentation are stored safely with role-based access controls. It also helps companies meet industry regulations by maintaining proper documentation, change logs, and audit trails.
- Drives process optimisation and innovation- You cannot improve what you cannot measure. Companies can organise and analyse engineering data to uncover process inefficiencies, spot quality issues early, and find new opportunities for innovation. Thus, it turns every day engineering activity into actionable business insight.
- Enables data reuse and design efficiency- One of the biggest advantages of engineering data management is the ability to search, reuse, and repurpose existing designs, documents, and components. This speeds up product development, reduces costs, and encourages best practices across engineering teams.
- Supports scalable growth and digital transformation- If you are adopting Industry 4.0, integrating IoT, or expanding globally, data management must scale with you. A modern EDM system grows with your organisation and integrates with your existing tools. It also sets the stage for automation, intelligent manufacturing, and AI-driven insights.
Key Components of an EDM System
When your engineering team moves among thousands of CAD files, test reports, and compliance documents, you need more than a basic folder structure.
A well-structured engineering data management system is built on key components that work together to ensure your data is organised, accurate, secure, and usable across the entire product lifecycle.
The key building blocks that you should know are as follows:
1. Data Governance and Policy
It forms the core of any engineering data management process. Data governance states the rules, responsibilities, and standards around how engineering data should be collected, accessed, stored, and protected.
It certifies that everyone, from engineers to managers, follows a consistent approach. Strong governance policies also help maintain compliance and safeguard intellectual property across departments and regions.
2. Data Acquisition and Capture
This component focuses on collecting engineering data from tools like CAD software, IoT devices, simulations, or test labs. It also makes certain that the data is validated and accurate before it enters your system.
Capturing reliable data upfront minimises errors down the line and lays the groundwork for better decisions and designs.
3. Data Storage and Organisation
After capturing the data, you need a scalable system to store and retrieve it easily.
A modern engineering data management software uses structured storage (on-prem or cloud) with data classification, taxonomy, and secure access control. This keeps sensitive information safe and allows teams to find what they need and why they need it quickly, without digging through disorganised folders.
4. Data Integration and Analysis
Engineering data, like design tools, ERP systems, and test labs, lives in many places. Integration connects all these systems so that data flows seamlessly.
This component uses ETL tools or APIs to unify the data. Once integrated, teams can use analytics, visualisation, and even AI to discover trends, optimise workflows, and make faster and smarter decisions across the brand.
5. Data Maintenance and Lifecycle Management
Your data needs care, even after it has been used. Lifecycle management includes version control, backups, archiving, and change tracking. It preserves historical data, traces the changes, and retains or disposes of information based on policy.
This not only supports compliance but also enhances auditability and continuous improvement in engineering workflows.
Therefore, a well-rounded engineering data management system brings these components together to eliminate chaos, drive collaboration, and boost productivity.
Engineering Data Management Process
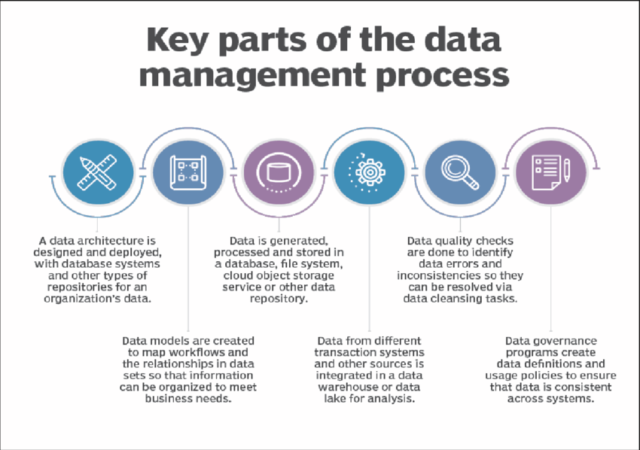
Source: ResearchGate
Managing engineering data is a well-organised and repeatable process. It makes certain that every piece of data flows smoothly, remains accurate, and supports innovation. From policies to analytics to version control, each stage is important to deliver high-quality products faster and with fewer errors.
Here is the complete engineering data management process:
- Data Capture- Engineering data is generated constantly from CAD software, simulation tools, sensors, production lines, and even supplier systems. Capturing this data accurately and in real time certifies that no piece of critical information is lost. Poor capture leads to garbage-in and garbage-out situations, which no engineer can afford.
- Data Classification- Once the data is captured, it must be organised. Classification is the process of tagging and labelling data based on its type, status, or use case. Smart engineering data management practices here reduce search time, help avoid duplication, and make compliance reporting easier.
- Data Storage- Centralised storage keeps everything in one secure place. A well-structured system not only maintains data security but also supports version control, backup, and disaster recovery. Your team will not waste time looking for files or second-guessing which version is correct.
- Access Control- Everyone should not have access to everything, thus the engineering data management system gives role-based access. It helps limit who can view, edit, or delete critical data. This not only reduces the chances of costly mistakes but also unwanted data leaks particularly for tighlty regulated industries like aerospace or medical devices.
- Sharing and Collaboration- Once your data is organised and structured properly, it is time to put it to work. Modern systems let you share information across the design, production, manufacturing, and quality control teams. Real-time access makes sure that everyone works with the latest data, which in turn, speeds up decisions and reduces back-and-forth errors.
Best Practices for Engineering Data Management
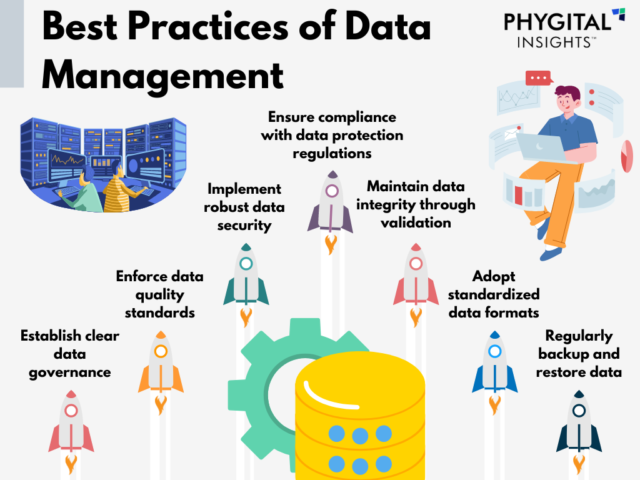
Source: Phygital Insights
Managing complex engineering data helps you stay ahead of mistakes, delays, and compliance risks. That is why following tried-and-tested engineering data management practices can help your team work faster and make smart decisions:
- Standardise your data structures- You can create file name conventions, version control rules, and classification standards to avoid confusion and duplication. A consistent structure make data easy to find and trust, which is key for scaling any engineering data management strategy.
- Implement role-based access control- Every team member does not need complete access. You can set up permissions based on roles to protect sensitive information and reduce the risk of accidental changes. This is especially critical when you are working with external vendors or cross-functional teams.
- Automate the process- Manual tasks slow teams down and increases the chances of human error. Automation streamlines the engineering data management process, approvals, document routing, and alerts. Many PLM systems come with built-in workflow tools to help you fulfill tasks fast, reliably, and with accountability.
- Enable real-time collaboration- In a hybrid work environment, your data system needs to support real-time file access, comments, and updates. When engineers, designers, and manufacturers work off the same version, it eliminates delays and miscommunication.
- Back up your data regularly- Data loss can cost you both time and trust. A strong engineering data management software includes regular and automated backups. Hence, you should look for tools that offer secure cloud storage, version history, and one-click restoration.
- Review and audit regularly- You should set regular check-ins for data. Reviews assist you in spotting outdated files, security issues, or broken access rules before they become bigger problems. It also helps you stay aligned with industry standards like ISO, FDA, or AS9100.
Engineering Data Management Software & Tools
Modern engineering data management depends on having the right tools in your corner. They are essential to scaling, securing, and speeding up your operations.
Some of the tools that help in the success of engineering data are:
- Database Management Systems (DBMS)- Oracle, SQL Server, MySQL, and PostgreSQL are the foundation for structured engineering data management. They offers fast and reliable access and ensure data stays intact. Built-in query languages make it easy to extract exactly what you need when you need it.
- Big Data Tools- If your projects involve sensor data or IoT devices, you can use Hadoop and Spark tools. Hadoop’s file system handles massive data storage, while Spark delivers lightning-fast processing. These tools are important for managing complex and unstructured datasets in Industry 4.0.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Tools- Power BI, Tableau, and QlikView turn raw data into interactive dashboards in any engineering data management system. These tools give engineers and managers instant visibility to make data-backed decisions with confidence.
- Data Visualisation Platforms- Communicating complex data across teams in different department can be tough. D3.js, Plotly, or Tableau are tools that can simplify this by converting data into charts, graphs, and maps, so everyone stays on the same page without a long explanation.
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) Tools- If you need to clean up data from multiple sources, Talend, Informatica PowerCenter, and Microsoft SSIS can automate that process. They provide consistency across platforms and reduce the risk of errors due to mismatched or outdated data.
- Cloud Storage & Computing- Cloud platforms like AWS and Google Cloud make engineering data management software scalable. They let you store massive datasets and run simulations without buying new hardware. Plus, global teams can collaborate in real-time, no matter where they are.
- IoT & Sensor Data Management- AWS IoT, Azure IoT Suite, and Google Cloud IoT help collect and analyse real-time data instantly. That is how you improve uptime, optimise performance, and make better maintenance calls before a breakdown happens.
Challenges in Engineering Data Management
It is not easy to manage large amounts of data from CAD files, simulation outputs, IoT sensor data, and BOM spreadsheets. If you do not have a solid plan, data chaos can slow your teams, create costly errors, and hamper innovation.
The following are the biggest challenges companies face with engineering data management:
- Data silos across departments- When all the design, manufacturing, and quality teams use different tools and platforms, important data gets trapped in silos. It leads to duplication, miscommunication, errors, and missed deadlines. A unified EDM system allows everyone to work with the same accurate information.
- Version control problems- It can be a costly mistake if multiple engineers work on outdated versions of the same file. When you do not have proper version control, teams waste time and risk errors. Thus, maintaining a single source of truth is essential for efficiency and accuracy.
- Security and IP protection risks- Engineering data like proprietary designs, simulations, or patents in progress is often highly sensitive. Poor security practices can expose data leaks, theft, or non-compliance fines. Hence, it is essential to implement role-based access controls and encryption.
- Poor data quality- Gartner reports state that companies with poor data quality incur an average cost of $12.9 million every year. It can also cause project delays or product failures. But when you have clean data, you can make confident decisions.
- Manual data entry and errors- If you are still relying on spreadsheets or manual uploads, it can lead to mistakes. Manual entry eats up valuable time and introduces human error. Automating data capture and syncing across platforms helps eliminate these issues.
- Scalability issues- What works for a 5-person engineering team does not always scale to 500. Many legacy systems cannot handle the growing volume and complexity of modern data. Scalable engineering data management systems built on cloud or hybrid infrastructure solve this by growing with your team and your data needs.
Future of Engineering Data Management
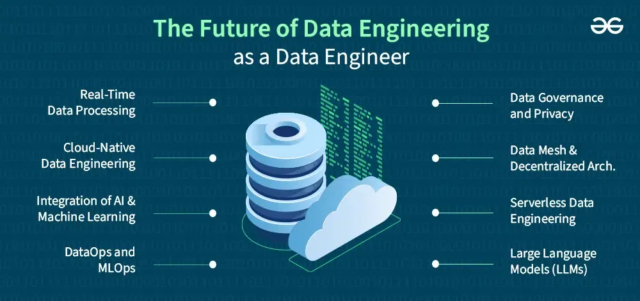
Source: GeeksforGeeks
Engineering is evolving rapidly, and so is the way we handle data. With increasing AI and IoT integration, the future of engineering data management unlocks real-time intelligence, automation, and smarter collaboration.
Here is what you can expect as we move into the next phase of innovation:
- AI-enabled data insights- Artificial intelligence revolutionises how engineers manage and use data. From predictive analytics to automated error detection, AI tools can process massive datasets, find patterns, and suggest improvements, which can save time and boost product quality. You can also expect more engineering data management platforms to integrate machine learning models that learn from your workflows.
- Cloud-first architecture- Cloud adoption is rising across industries, and engineering is no exception. According to Gartner, integrating the cloud will be a necessity in businesses by 2028. A cloud-based engineering data management system offers scalability, real-time collaboration, and remote access, especially for remote teams.
- Tighter IoT integration- Smart factories and connected products generate a lot of sensor data. The ability to capture, process, and act on this data in real time will become central to the future of engineering data management. This will support predictive maintenance, real-time product testing, and closed-loop feedback systems between design and production.
- Digital twin technology- Virtual replicas of physical products are quickly becoming mainstream. They rely on continuous data input from various sources to simulate real-world conditions. Managing this data effectively will require more advanced engineering data systems that are capable of handling dynamic and multi-source data flows in real time.
- Stronger focus on data governance- As data volumes grow, the regulatory and security challenges grow with it too. In the future, companies will emphasise data governance by creating clear policies for who owns, accesses, and modifies engineering data. You can expect more built-in compliance features in tools, so that your data management is efficient, secure, and audit-ready.
Conclusion
The days of managing files in scattered folders or relying on outdated systems are over. As digital transformation reshapes industries, engineering teams need systems that support real-time access, accurate version control, compliance, and cross-functional collaboration.
Engineering data management is the best approach for designing a product, streamlining manufacturing, or collaborating across teams. It also reduces errors, speeds up time-to-market, and fosters stronger innovation.
So, invest in strong engineering data management foundations today!



