
Introduction
Today, buyers move fast, jump across channels, and expect personalised experiences at every touchpoint. They scroll your Instagram, Google your reviews, visit your site, compare you to three competitors, chat with support, and then decide to buy.
Traditional funnels are falling short. You need real-time data from every touchpoint to understand what is driving results and what is blocking them.
This is where customer journey analytics can help you see all interactions a customer has with your brand before, during, and after a purchase.
In this guide, you will discover what customer journey analytics is, how it is different from journey mapping, and why B2B brands are obsessed with it. We will also break down practical steps, must-track metrics, and tools to help you analyse what your customers actually do.
What is Customer Journey Analytics?

Source: QuestionPro
The practice of understanding how people interact with your brand across different channels is known as customer journey analytics.
From the moment someone first hears about your business to long after they make a purchase, this practice shows the full picture. Be it website visits, app interactions, social media clicks, and customer service calls, all these allow you to understand your customers’ behaviour.
A McKinsey report shows that companies using customer journey analytics software see faster customer satisfaction and a 10-15% increase in revenue. It is because the tool helps them make data-driven decisions.
You can consider it an upgrade to the traditional customer journey mapping. While mapping shows a theoretical path, analytics shows the actual user behaviour and interactions.
The user journey analytics focuses more on behaviour patterns within a specific product or session rather than the full and multi-channel experience.
Why is Customer Journey Analytics Important?
Customers interact with brands across different channels, such as social pages, emails, or apps. If you are not tracking those interactions strategically in a connected way, you will miss out on several growth opportunities.
Following are the advantages of using customer journey analytics:
- See the entire customer journey- Most users do not go from ad to purchase in one click. The path is non-linear, which involves multiple channels and devices. With customer journey analysis, you can track every interaction, such as likes, email opens, chats, and website visits. You can see the actual steps they take and get a clear view of what is working and what is not.
- Identify pain points and bottlenecks- If many customers leave during checkout, CJA can show where they are dropping off exactly. This way, you can address issues like slow load times, confusing forms, or unexpected costs and provide a smooth purchase experience.
- Create personalised customer experiences- 80% of consumers prefer brands that offer personalised experiences. Customer journey analytics helps you tailor your messages, offers, and experiences to what your audience actually wants.
- Boosts conversions and reduces churn rate- When you understand user behaviour at every step, you can optimise your offering with what matters the most. This way, you can increase your conversion rate and build a smooth experience that keeps customers coming back.
- Make smarter and data-driven decisions- Instead of acting on assumptions, customer journey analytics assists you in acting on real behavioural insights. That is how brands evolve from reactive to proactive and see long-term growth.
- Maximise ROI on campaigns- All the touchpoints do not contribute equally to conversions. With CJA, you can spot which campaigns, channels, or tactics drive the most impact and reallocate budget accordingly. It, in turn, gives higher ROI and lower wastage of resources.
Customer Journey Analytics vs Customer Journey Mapping
People often confuse customer journey mapping with customer journey analytics. While both are important, one helps in visualising user behaviour, and the other deals with real data.
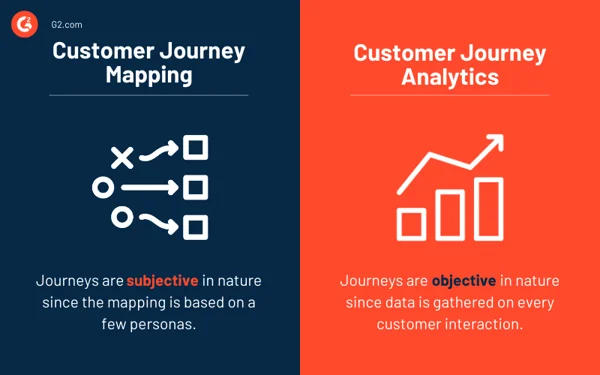
Source: G2 Learning Hub
What is Customer Journey Mapping?
Storyboarding your customer’s experience from the first brand interaction to conversion or advocacy is called customer journey mapping. You can consider it a storyboard for how your customer experiences your brand.
These maps include:
- Each stage of the journey
- Key touchpoints (like website visits, email opens, or in-store visits)
- Expectations and emotions of customers at each stage
- Metrics such as NPS or CSAT
- Real-time feedback that showcase pain points or highlights
The Role of Customer Journey Analytics
While mapping shows the visual picture, customer journey analytics works on the data.
It collects and analyses data from every customer interaction to see what is working, what is not, and where customers drop off. Unlike static journey maps, journey analytics are dynamic and driven by real-time behaviour.
For example, if analytics show that customers are abandoning their cart after viewing the shipping page, you know exactly where to investigate and what to fix.
Key Difference (and How They Work Together)
The simple way to think about it:
Mapping is what we think the customer journey looks like.
Analytics is what the customer journey actually is.
They complement each other perfectly. You start with a map and then layer it with customer journey analysis to validate and optimise. When you use both of them together, you will get the strategic overview and the tactical insights to improve CX at every step.
Key Metrics & Data Points to Track
Now that you have understood what is customer journey analytics, you must know what to track to make all the difference between scattered data and actionable insights.
Some of the most important metrics and data points that you should monitor to understand and improve your customer journey are:
- Touchpoint Conversion Rates- It tells you how many users move from one stage of the journey to another. These insights help you understand where the buyer behaviour changes and what you should prioritise for improvements.
- Customer Retention Rate (CRR)- CRR tracks how many customers return after their first purchase and helps measure loyalty. A solid retention strategy usually comes from consistent positive customer experiences across all touchpoints.
- Time to Conversion- Time to conversion in user journey analysis shows the time taken to go from awareness to purchase. It reveals how efficiently your funnel guides users to take action.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT)- CSAT score measures how happy customers are at specific points in their journey. It is useful for spotting weak links in your support or onboarding experience.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)- Net Promoter Score tracks how likely customers are to recommend your brand to others. It helps you understand how satisfied and emotionally connected they are with your business.
- Churn Rate- If customers are leaving, you must know when and why they are leaving. Customer journey analysis helps tie churn to specific interactions, so you can take proactive steps.
Stages of the Customer Journey
A series of connected interactions that shape how people feel about your brand defines the customer journey. When you understand those stages, you can build stronger relationships and encourage repeat business.
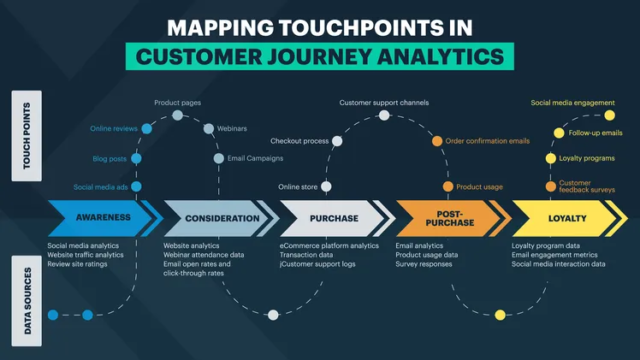
Source: Kapiche
The fundamental stages of the customer journey are as follows:
Stage 1: Awareness
When your customer hears about your brand for the first time through a social media post, an ad, or a friend, they are at the awareness stage. For instance, someone might see a sponsored post on Instagram for reusable water bottles and click to learn more.
In this stage, your messaging should be simple, clear, and genuinely helpful to grab the customer’s attention.
Stage 2: Consideration
In the consideration stage, customers evaluate whether your product or service fits their needs. They read reviews, watch product demos, or download guides.
You can use customer journey analytics to see which content drives the most engagement and bounce rate at this stage.
Stage 3: Decision
Your buyer is ready to convert at the decision stage. Here, your brand should provide a smooth experience with a user-friendly checkout, clear pricing, and real-time support.
A meaningful user journey analysis will show if customers abandon carts or get stuck at payment screens.
Step 4: Retention
After the purchase is made, your business’s focus should be on building loyalty. You can send helpful onboarding emails, ask for feedback, and offer support to drive engagement and loyalty.
Stage 5: Advocacy
If you have happy customers, chances are that they will be your biggest promoters. They leave reviews, refer friends, and talk about your brand on social media.
Customer Journey Analytics Software and Tools
Aberdeen Group found that companies that use customer journey analytics software show 54% more ROI. When you use the right tools, you can spot what is working and what is not in real time.
Here are some of the most popular tools that help you turn raw data into actionable insights:1. Google Analytics 4 (GA4)- Google Analytics 4 measures the behaviour of the user across different websites and apps. It helps you see how people move through your site and where they leave. With the help of GA4, you can track events like clicks or purchases, which makes it easier to spot obstacle points or drop-offs. It is a wonderful tool for user journey analysis across platforms.
Source: Backlinko
- Adobe Customer Journey Analytics- Adobe CJA is a sturdy tool for enterprise businesses that want deep insight into cross-channel performance. It integrates data from multiple sources, such as web, mobile, and CRM. Through Adobe CJA, you can segment audiences, track behaviour in real time, and build customizable dashboards.
- Mixpanel- Mixpanel is popular for analysing product usage and customer retention through funnel analysis, A/B testing, and cohort reports. These features are useful for apps and SaaS products that want to improve how users onboard and stay engaged.
- Hotjar- Hotjar help you learn how users interact with your website with the help of heatmaps, surveys, and session recordings. It shows what users do and why they do it. This adds emotional context to your customer journey analysis, particularly in the consideration or decision stages.
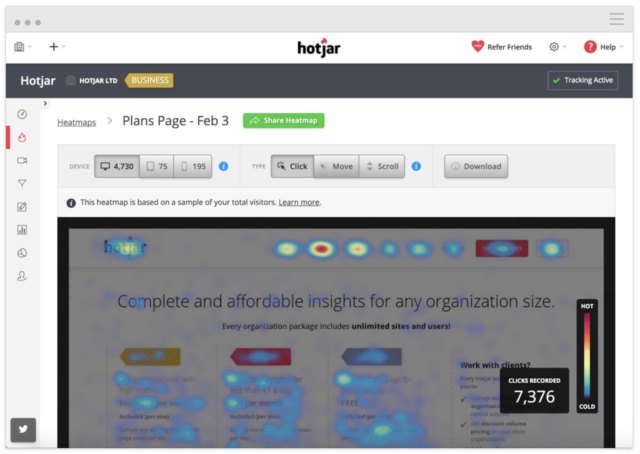
Source: Knapsack Creative
- Heap- Heap captures all user interactions through clicks, form fills, and page views, without minimal tagging. This way, it becomes easier to build full customer journey reports and identify trends or drop-off points quickly.
- Qualtrics CustomerXM- If you want a tool that focuses on customer feedback and experience metrics, Qualtrics is a perfect choice. It combines behavioural data with survey responses to give a 360° view of the customer journey.
How to Conduct Customer Journey Analysis
Source: Insider
Customer journey analytics help you discover the actual path your customers take. Here is a step-by-step way to conduct the analysis of the customer journey:
Step 1: Start with Clear Goals
Before diving straight into the data, you need a goal. You may be trying to fix a drop in conversions, improve onboarding, or reduce churn, but defining a single and measurable goal is essential.
Without a clear goal, your analysis becomes incomplete. So, you should start small, focus on one part of the funnel, and then go deep. This will keep your efforts aligned and your insights actionable.
Step 2: List Every Customer Touchpoint
The next step is to list places where your customer interacts with your brand, like website visits, social media comments, chatbots, and even in-store experiences. Tracking these touchpoints is important for user journey analytics. If you miss any of them, you will miss the context.
So, you should get input from marketing, sales, and support teams as they often see different sides of the same customer journey. The more complete your touchpoint list, the better your map will reflect reality.
Step 3: Dig into the Data
Now that you have a list of all the customer touchpoints, it is time to extract the data. You can use Google Analytics, Mixpanel, or Hotjar to see what customers do and where they get stuck.
Then, check bounce rates, click paths, time on site, and cart abandonment, read customer reviews, and talk to support teams.
Step 4: Segment Your Audience
Treating every customer the same is the worst mistake that businesses make.
People behave differently depending on who they are, where they are, and what they want. So, break them into segments, like new vs returning visitors, mobile vs desktop users, and high-spending vs low-spending.
Segmentation helps you spot trends and tailor experiences that actually convert. When done right, this step can reveal hidden friction that is invisible in the big picture.
Step 5: Map the Journey Visually
Journey mapping is significant in customer journey analytics to see the real journey moving forward. Miro, Lucidchart, or Smaply are some of the wonderful tools that you can use to build a visual map that includes actions, emotions, pain points, and decision triggers.
A great map helps align your team and spot opportunities instantly. It means you will see things you could not see before with raw data alone.
Step 6: Spot the Bottlenecks
Data without action will lead to failure. Hence, it is time to identify where people are dropping off and which steps make them hesitate. Chances are that your pricing page is confusing, or the checkout takes too long.
These pain points are where your improvements will have the biggest payoff. All you need to do is pick one high-impact change, implement it, and measure. This way, the customer journey analysis becomes a revenue machine.
Step 7: Test, Improve, and Repeat
Customer journeys change as your business grows, tech evolves, and customer needs shift. So, you should treat user journey analysis as an ongoing process.
Test new ideas with different CTAs, layouts, and personalised emails. Then, measure what works and double down. This cycle of testing and refining is how brands like Amazon and Netflix became customer-obsessed giants.
Customer Journey Analytics Examples
Understanding how customers behave at different stages is important to improve experiences and boost conversions. Here are some practical customer journey analytics examples to show how brands can use data to their advantage:
- Funnel Analysis to Spot Drop-Offs- Track how users move through stages like sign-up, onboarding, or checkout. When users drop off, funnel reports help pinpoint where things go wrong. You can also combine it with session recordings to see exactly what the user experienced.
- Path Analysis to Discover Optimal Journeys- Path analysis tracks non-linear behaviour. It shows the exact steps users take towards a goal. This helps you find the most efficient path and remove obstacles along the way.
- Heatmaps to Monitor Feature Engagement- You can use heatmaps to see where users click, scroll, or hover. This reveals which features attract attention and which are ignored. You can also use this insight to guide users toward valuable features with in-app messages.
- Product Trend Analysis to Improve Retention- Spot trends that indicate when users are stuck or frustrated. For example, if users engage with a feature but do not complete a task, that is a sign that something needs fixing. This is a powerful method of customer journey analysis.
Final Thoughts
Understanding your customers at every step has become important.
Customer journey analytics is the best way to track, analyse, and improve every interaction a customer has with your brand. From the first touchpoint to long-term loyalty, it helps businesses identify friction points and take action before customers drop off.
It acts as a secret weapon that smart businesses use to deliver personalised experiences, reduce churn, and grow faster.
So, if you have not started analysing your customer journey yet, now is the time!



